The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) cited research reports by British researchers that the mutation covid-19, the "Kent" variant, which was discovered in the United Kingdom in September last year and is now widely spread across the United Kingdom, seems to be undergoing some new mutations in British.
In the testing of some virus samples, British researchers found that some new coronavirus samples had a mutation called E484K. This mutation had previously appeared in the mutant new coronaviruses found in South Africa and Brazil, and it has also naturally appeared in The first mutated new coronavirus was discovered in Kent, southern England.
The BBC reported that experts from the Public Health Department of the United Kingdom have so far only found that 11 of the 214,159 virus samples they have tested have the E484K mutation, which means that the mutation is not yet widespread. The UK has already taken measures to control the spread of the new coronavirus. Some parts of England have even begun to carry out emergency testing of the mutant virus found in South Africa, and introduced travel restrictions to prevent more cases from being imported from abroad.
Julian Tang, a virus expert at the University of Leicester in the United Kingdom, said that it is important that people abide by the regulations of the lockdown and reduce the number of infections, otherwise the virus will not only continue to spread, but also continue to evolve. Allowing the virus to spread widely will provide different emerging variants. A "melting pot".
However, the current number of vaccines is limited, and the effect has not been confirmed. Before the vaccine became popular, wearing a mask was the most effective way to prevent the epidemic. Many people even make masks at home. So, what materials are needed to produce masks?
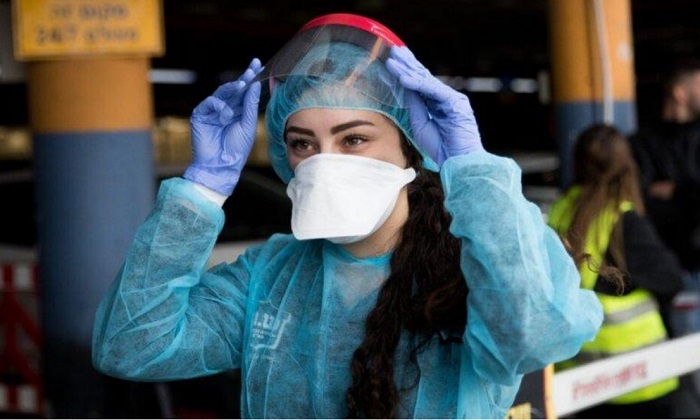

The composition of the mask
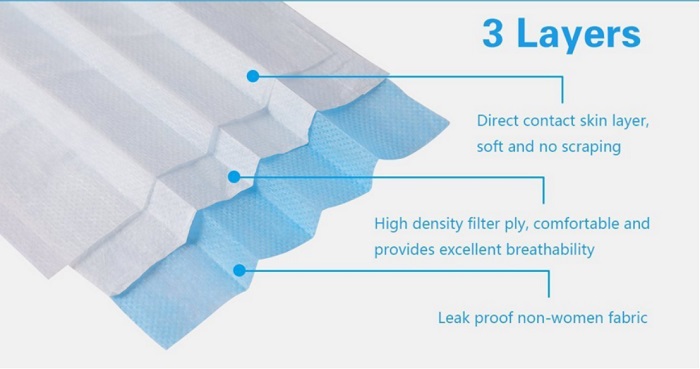
The raw materials of masks are mainly non-woven fabrics, including spunbond non-woven fabrics and meltblown fabrics. The mask is divided into three layers, the outermost and innermost layers are spunbond non-woven fabrics, and the middle layer is meltblown fabric. Spunbond non-woven fabrics mainly block dust and large particulate matter through mechanical isolation, and the pores between the meltblown fibers are more dense, which can mechanically block small particulate matter and block viruses through electrostatic adsorption.(try Suntech mask machine)
What is the output of non-woven fabrics and is it sufficient for mask production?
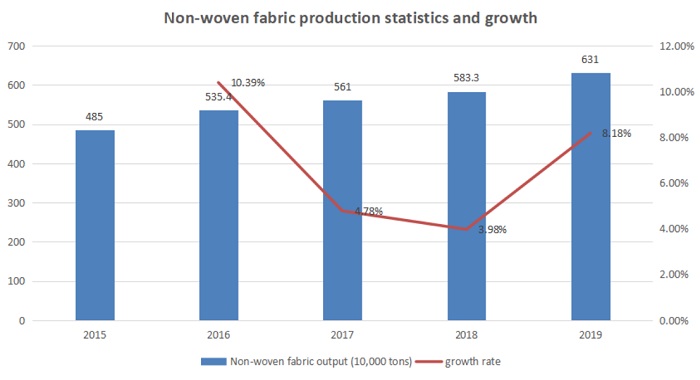
Non-woven fabric, also known as non-woven fabric, is composed of oriented or random fibers. In recent years, the non-woven fabric industry has developed rapidly in China, and China has become the world's largest non-woven fabric producer and consumer. In 2018, China's total non-woven fabric production reached 5.932 million tons. In 2019, the total non-woven fabric production reached 6.31 million tons, accounting for 37.91% of the global non-woven fabric production, an increase of 5.7% year-on-year. In 2019, the output of non-woven fabrics of enterprises above designated size in the industry reached 5.03 million tons, a year-on-year increase of 9.9%.
The non-woven fabric industry has the characteristics of short process flow, high output, low cost, rapid variety change, and extensive raw material sources. According to its process, non-woven fabrics can be divided into spunlace non-woven fabrics, heat-bonded non-woven fabrics, pulp air-laid non-woven fabrics, wet-laid non-woven fabrics, spunbonded non-woven fabrics, meltblown non-woven fabrics, needles Stab non-woven fabric, stitch-bonded non-woven fabric, etc.
In 2018, China's non-woven fabric market was dominated by spunbonded non-woven fabrics, with an output of 2.971 million tons, accounting for 50.09%; the output of needle punched non-woven fabrics was 1.362 million tons, accounting for 22.96%, which is worth Note that the output of meltblown cloth, the core component of masks, accounts for only 0.9%.
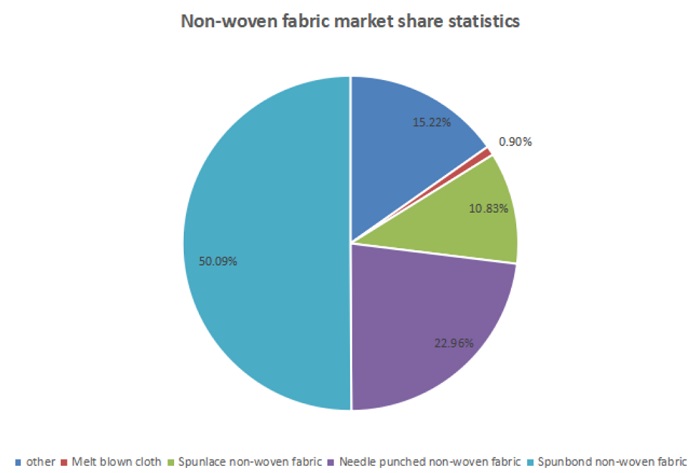
It can be seen that the current output of spunbonded non-woven fabrics is still relatively large, enough to supply mask production, and meltblown fabrics are relatively short.(try Suntech Melt blown machine)
Characteristics and uses of spunbond non-woven fabrics
Spunbond non-woven fabric: After the polymer is extruded and stretched to form continuous filaments, the filaments are laid into a web, and then through self-bonding, thermal bonding, chemical bonding or mechanical reinforcement methods, the web becomes Non-woven fabric. The main materials of spunbond non-woven fabrics are polyester and polypropylene.

(Suntech ST-ASS spunbond nonwoven)
Features:
Good high temperature resistance, good low temperature resistance (polypropylene can be used for a long time in an environment of 150 ℃, polyester can be used for a long time in an environment of 260 ℃), aging resistance, UV resistance, high elongation, good stability and air permeability, corrosion resistance , Sound insulation, mothproof, non-toxic.
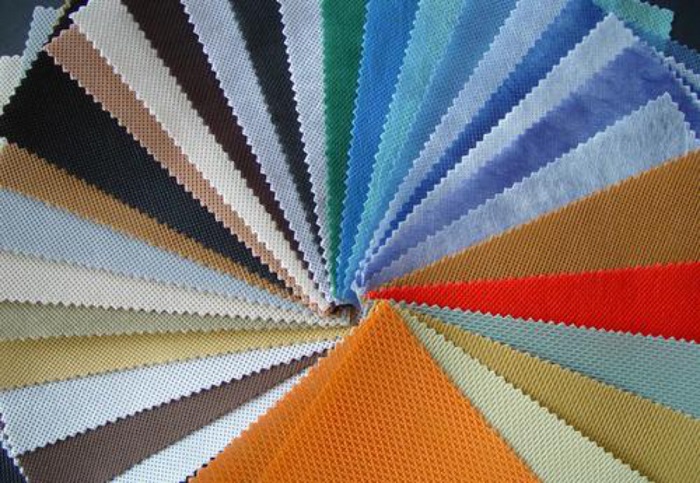

Application:
The main products of spunbond non-woven fabrics are polypropylene and polyester (long fiber, staple fiber) non-woven fabrics. Common applications are non-woven bags, non-woven packaging, flower packaging cloth, luggage cloth, masks, etc.,There are also a wide range of applications in hygiene, environmental protection filtration, geotechnical construction, automobiles, artificial leather, packaging and clothing.
Spunbond non-woven fabrics have been widely used in non-durable clothing, such as spunlace medical protective clothing, PP disposable spunbond protective clothing and SMS medical protective clothing. According to the degree of durability, clothing is divided into two categories: durable and non-durable/disposable clothing. At present, the application of hot-rolled non-woven fabrics in clothing is mainly concentrated in the field of non-durable clothing.
Spunbond non-woven fabrics are easy to identify, and generally have good two-way fastness. Generally, spunbond non-woven fabrics have diamond-shaped nip points.

Spunbond non-woven fabric process
Polypropylene:polymer (polypropylene + recycled material)-large screw high temperature melt extrusion-filter-metering pump (quantitative delivery)-spinning (spinning entrance up and down drawing suction)-cooling- Air traction-net formation-upper and lower pressing rolls (pre-reinforcement)-hot rolling (reinforcement) of rolling mill-winding-inverted cloth slitting-weighing and packaging-finished product storage
Polyester:processed polyester chips-large screw high temperature melt extrusion-filter-metering pump (quantitative delivery)-spinning (up and down drawing and suction at the spinning inlet)-cooling-air traction ——Net formation——Upper and lower pressing rolls (pre-reinforcement)——Hot rolling on rolling mill (reinforcement)——Winding——Inverted cloth slitting——Weighing and packaging——Product storage

Spunbond non-woven fabric development history
Spunbond is a kind of non-woven fabric technology. It is a continuation of the synthetic filament spinning process commercialized in the 1940s and 1950s, and its origin can be traced back to the 1940s. In the early 1950s, the U.S. Naval Laboratory established a small melt extruder to extrude the melted polymer from the spinneret holes to form very fine filament fibers, which were then blown to netting curtain, the fibers are bonded into a net. This is the earliest spinning technique. However, due to the limitation of the technical level at that time, this technique could not be studied.
With the development of chemical fiber technology, the Freudenberg company in Germany and Dupont company in the United States began to study spunbond nonwoven technology in the late 1950s. However, due to high production costs and imperfect technology, technical results were not available promoted.

It was in the 1960s that the American Du-pont Company applied for a patent, and industrial production began in the mid-1960s. In the late 1960s and early 1970s, spunbond non-woven fabric technology was developed. The German Reifen company adopts an integral horizontal Venturi drafter, which has greatly improved the quality of spunbonded non-woven fabrics, and the degree of industrial production has also been greatly improved. In the future, American Aisen Company will apply meltblown technology to spunbond technology. Due to the special structure of the drafter, this has enabled the spunbond non-woven technology to have greater development.
Due to the rapid progress of spunbond production technology, high growth rate, large production capacity, high quality, excellent performance, wide product application range, strong market adaptability, and the short production process of spunbond non-woven fabrics, high production efficiency , with the advantage of large-scale production, among which the strength and elongation of the spunbonded non-woven fabric is better. At present, with the emergence of differentiated fiber spinning technologies such as meltblown and spunbond multi-nozzle composite technology, bicomponent, etc., it has brought broader application prospects to spunbond nonwoven technology. Therefore, the nineteenth century After the ten years, spunbond non-woven fabrics have been developed more rapidly and widely in terms of product use and technological advancement.
At present, the world's spunbond non-woven fabric technology mainly includes the Reichfell technology of Germany, STP technology of Italy, and Kobe Steel technology of Japan. The current situation, especially the Refine technology has become the mainstream technology in the world. Has developed to the fourth generation of technology. The characteristic is that it adopts negative pressure ultra-high speed air drafting, and the fiber can be stretched to about 1 denier.

With spunbond non-woven technology, spunbond non-woven equipment is also needed. Suntech has developed and manufactured intelligent spunbond non-woven machines with 50 years of technical precipitation and design experience. The production efficiency is high, and the intelligent design allows labor Cost savings. The core component spinneret adopts Japan's leading technology, using German Demagi CNC machining center and Italian Fidia gantry five-axis high-speed milling, and it is polished by fluid. The hole diameter can reach 0.45mm, the air drawing is 1-4μm, and the spinning is fine. And uniform, enough to ensure the filterability and air permeability of the material, please inquire for details.




