Ancient textile culture has a long history
Ancient Chinese textiles have gone through a long and glorious history. Primitive Gehe, pristine cotton, and luxurious silk appeared one by one, interpreting scenes of splendid and splendid pictures. From the legendary originator of sericulture and silk extraction, Lei Zu, to Ma Jun who improved textile machinery, to Huang Daopo, a peasant woman who spread cotton spinning technology, to the handed down masterpiece "Heavenly Creations", the history of ancient Chinese textiles has been continuously rewritten and made achievements. Brilliant and splendid achievements. Different from the simple and unpretentious history of traditional agricultural tools, different from the history of water conservancy projects that benefit the people, and also different from the history of animal husbandry where the six animals are flourishing, the history of ancient Chinese textiles is more colorful and splendid, and more gorgeous and warm.
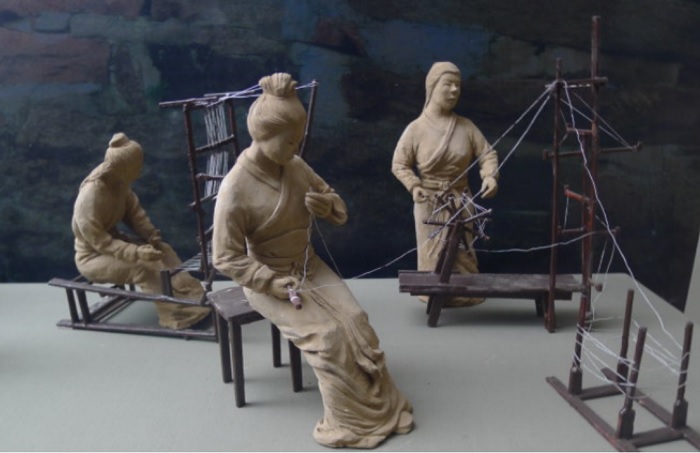

The primitive ancestors learned to use kudzu fiber, stone knives, bone cones, etc. to make primitive clothing that covered the shame body from the initial finger-hanging of the hand sutra. This was the earliest textile prototype. With the formation of primitive textile prototypes, textile tools came into being. Many stone, pottery, wooden, and bone primitive textile tools and wooden loom parts were unearthed at the Hemudu site in Yuyao, Zhejiang. Some bronzes unearthed in the Xia and Shang dynasties have obvious fabric traces on them, and a small amount of clothing fragments are also unearthed. These traces and physical objects show that the textile fiber raw materials of this period were mainly silk and hemp. Hemp, ramie and kudzu become the main plant fiber raw materials.
The exquisite silk was born in the middle and late Neolithic period. The Yangshao cultural purple color Luo unearthed in Qingtai Village of Xingyang, and the silk piece, ribbon and silk thread unearthed in Wuxing Qianshanyang are the most convincing material evidence. Since then, silkworms have been raised indoors, and the yield and quality of silk, the quantity and variety of silk have increased, and the supremacy of silk fabrics in the history of Chinese textiles has since been established.
During the Spring and Autumn Period and Warring States Period, the silk reeling tool developed from the initial manual silk reeling to the hand-operated silk reeling car and the pedal silk reeling car. Ma Jun, a well-known mechanical engineer in the Three Kingdoms period, carried out a major reform of the jacquard loom again after Chen Baoguang in the Western Han Dynasty, changing the 50-pin to the 12-pin, which became another major innovation in the history of Chinese textile technology and increased production capacity.
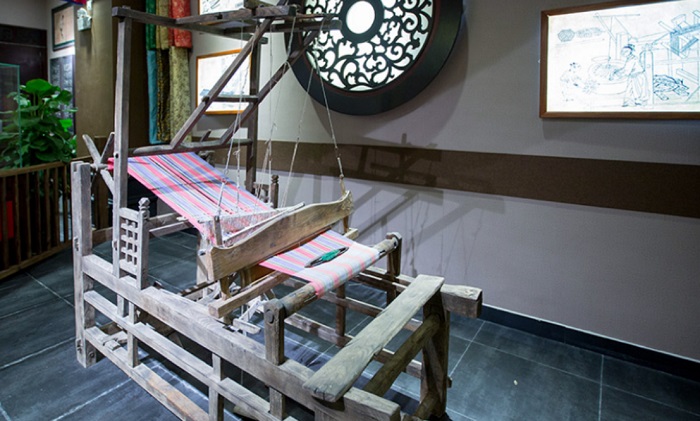

In the Ming and Qing Dynasties, sericulture silk was affected by cotton, but the sericulture production in Hangjiahu area was still relatively developed. Archaeological discoveries prove that the Ming and Qing dynasties continued to innovate in silk weaving, printing, dyeing, and embroidering techniques and patterns compared with the previous generations. From these archaeologically excavated textile garments displayed in the showcase, it can be seen that the embroidery and printing and dyeing techniques at that time have reached a very high level.
The cotton introduced to China in the Han Dynasty was still confined to some remote areas in the southwest and south in the Song Dynasty. During the turn of the Song and Yuan Dynasties, cotton production quickly spread in the mainland, and became the most basic raw material for clothing after the Yuan and Ming Dynasties. With the promotion of cotton cultivation, China's cotton textile technology has been further developed. Cotton textiles first emerged in Yunnan and Hainan Island, where ethnic minorities have long accumulated a set of cotton textile processing technologies.
In the early Yuan Dynasty, Huang Daopo introduced advanced cotton weaving technology learned from the people of the Li people in Hainan to the mainland, and improved tools such as rolling, elastic, spinning, and weaving, which greatly increased the spinning efficiency. In addition, she woven the famous Wunijing quilt with cross yarn, color matching, heald thread and other techniques, which promoted the development of cotton textile technology and the cotton textile industry in Songjiang, making Songjiang once the center of the national cotton textile industry at that time. . It can be seen that Huang Daopo's influence in the history of China's cotton textile development can be described as pivotal and far-reaching.
In the long-term textile production practice, people have invented many cotton textile processing machinery. From the deseed machine used in the initial cotton ginning process; the vertebral arch used to elasticize the deseed cotton; the most primitive tool used to spin and twist the thread-spinning, manual machine-spinning wheel (originally called weft Cars); pedal spinning wheels that have been improved afterwards; spindle racks, warp cars, and warp beds that facilitate the post-processing of cotton yarn; and looms for weaving processes. This is the embryonic form of textile machinery.

The first industrial revolution gave birth to mechanized looms
In the wave of the first international industrial revolution, the original looms could no longer meet the development needs of the textile industry, and they were gradually replaced by mechanical and automated looms.
One day in 1764, James Hargreaves, a weaver in Lancashire, England, changed history. He went home and opened the door and knocked down his wife's spinning machine. When he bent over to try to right the spinning machine, he found that the fallen spinning machine was still spinning. It's just that the original horizontal spindles have become upright. He suddenly thought that if several spindles were arranged vertically, a spinning wheel would drive them. Isn't it that the efficiency can be increased several times? The next day, he verified his idea and put 8 spindles vertically, which increased the efficiency by 8 times. And named the new spinning machine after her daughter, this is the Jenny spinning machine.
In 1770, the couple obtained a patent. In 1784, the Jenny machine could have 80 spindles. Four years later, the British Jenny machine had reached 20,000.
The appearance of the Jenny machine enabled the establishment of a large-scale weaving factory. In order to obtain reliable production power, people continue to explore and innovate boldly. As Watt's improved steam engine began to be used as a power source for textile machinery, the first industrial revolution also ushered in a climax.
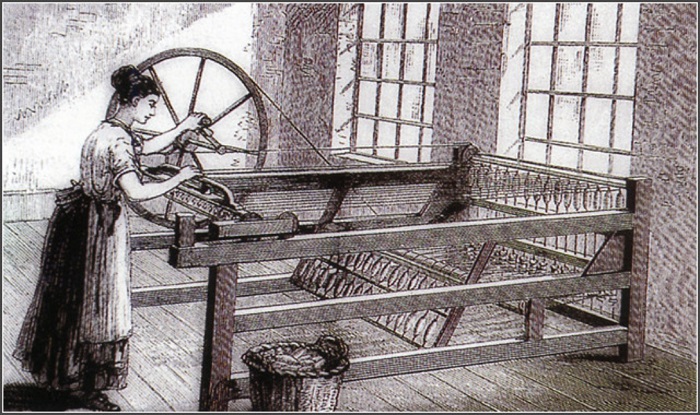
What is the current loom?
Nowadays, the textile machine has undergone earth-shaking changes. It has undergone mechanization, automation, and intelligence changes, and can simultaneously complete the five basic actions of weaving.
Opening mechanism
The warp yarn is divided into upper and lower layers to form a shed. There are cam (tread plate) shedding mechanism, dobby shedding mechanism and jacquard shedding mechanism. The pedal shedding mechanism uses cams to control the lifting and the sequence of the heald frame. Generally use 2-8 page heald frames, suitable for the production of various plain weave, twill weave, satin weave and corduroy fabrics. The dobby shedding mechanism is controlled by the broach, pull hook and heald rod to lift the heald frame, and the lifting sequence of the heald frame is controlled by the flower tube, the pattern plate, the nail, and the heavy tail rod. In order to weave various small pattern fabrics, 16-32 page heald frames can be used. The jacquard shedding mechanism (Figure 4 jacquard shedding mechanism) is controlled by the lifting knife, hook (or straight needle), heald, etc. to control the raising of the warp. Each warp can be raised and lowered separately; the warp raising is controlled by the kaleidoscope, pattern, horizontal needle, etc. order. This kind of shedding mechanism can weave fabrics with large patterns, such as jacquard towels, jacquard blankets, jacquard brocades, sceneries and other fabrics. A loom equipped with a jacquard shedding mechanism is called a jacquard loom.
Weft insertion agency
The mechanism that introduces the weft into the shed. On a shuttle loom, the weft is hit by the shuttle mechanism to make the shuttle fly into the shed. The picking mechanism is divided into three types: top pick, middle pick and bottom pick. Due to the violent impact of this kind of shuttle mechanism, the vibration and noise of the loom are large, the machine and materials are consumed too much, and it is not safe enough. Sometimes, accidents of flying shuttle may occur. On the shuttleless loom, the weft is introduced into the shed by the weft inserter. This kind of loom without shuttle eliminates the shortcomings of picking.
Beat-up mechanism
A mechanism that pushes the weft introduced into the shed to the weaving mouth. There are two main types: one is to use cranks and connecting rods to drive the reeds on the sley and move back and forth to perform beating-up. This is called a connecting rod beating-up mechanism; the other is to drive the reeds on the sley by a conjugate cam. It is called a conjugate cam beating-up mechanism for beating-up with forward and backward motion. The cam can be designed as required to control the static time of the sley at the rear, which is suitable for weft insertion and beating-up of broad-width looms.
Take-up mechanism
After the fabric is formed into the specified weft density, it is taken away from the work area and rolled onto the cloth roller. The fabric is usually wound up with a round roller covered with a friction material layer in a gear drive. The take-up mechanism can change the weft density of the fabric by changing gears.
Let-off agency
The mechanism for sending out the warp according to the weaving needs is usually composed of two parts: the warp sending device on the weaving shaft and the warp tension adjusting device. During the weaving process, the warp yarns are required to have proper tension on the machine, and the warp yarn tension should not fluctuate up and down with the change of the weaving shaft diameter.
In addition, there are various auxiliary devices on the loom to increase the output and fabric quality of the loom, reduce the labor intensity of the weaver, prevent damage to parts, and protect the safety of the operator. Such as weft yarn breakage automatic stop device, warp yarn breakage automatic stop device, warp guard device, flying shuttle guard device and so on. When the loom is equipped with an automatic shuttle changing mechanism, it is called an automatic shuttle changing loom; when it is equipped with an automatic changing mechanism, it is called an automatic shuttle changing loom. When weaving patterned fabrics with different wefts, a multi-shuttle box mechanism is installed on the loom, which is called a multi-shuttle loom. Multi-shuttle box looms are divided into single-side multi-shuttle box and double-side multi-shuttle box. Single-sided multi-shuttle box means that one side of the loom is a single-shuttle box, and the other side is a multi-shuttle box. For example, a 1×4 multi-shuttle box is a single-sided 4 shuttle box. Double-sided multi-shuttle box means that both sides of the loom are multi-shuttle boxes. For example, a 4×4 multi-shuttle box is a double-sided 4 shuttle box.
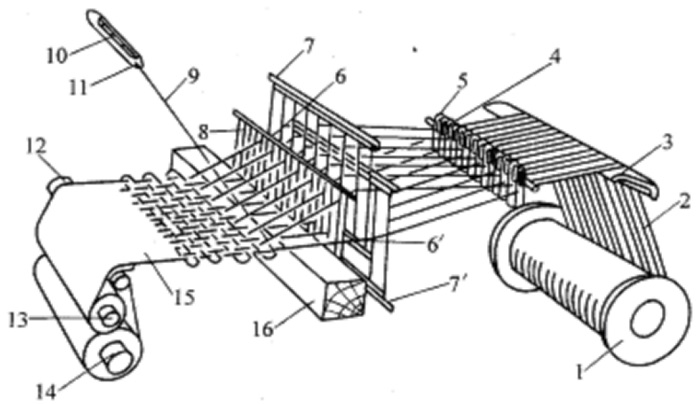
Weaving machine classification
There are various weft insertion methods for shuttleless looms, including rapier, jet (air jet, water jet), projectile, multi-shed (multiphase) and weaving.
- Rapier loom: use rigid or flexible rapier heads, belts to clamp and guide the weft. In addition to being suitable for weaving plain and textured fabrics, rapier looms are characterized by easy color change, suitable for multi-color weft fabrics, and suitable for the production of yarn-dyed, double-layered fleece fabrics, loop fabrics and decorative fabrics.
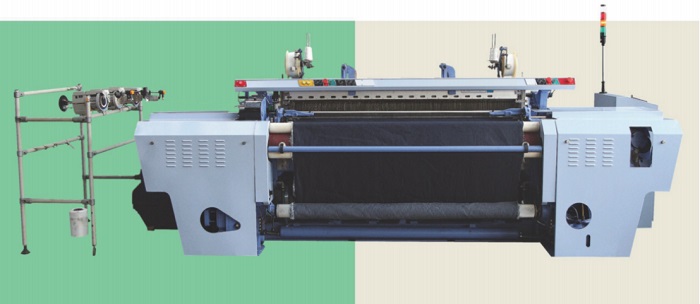
- Air jet loom: draw the weft yarn with the compressed air jet, and bring the weft yarn through the shed. The biggest feature of the air-jet loom is fast speed and high labor productivity. It is suitable for the production of plain weave and grain fabrics, fine ultra-high-density fabrics and large-volume fabrics.

- Water jet loom: Use water as the weft insertion medium to generate frictional traction on the weft with the jet of water, so that the weft on the fixed package is introduced into the shed. The water jet loom has the characteristics of high speed and high unit output. It is mainly suitable for the production of hydrophobic filament chemical fiber fabric with smooth surface.
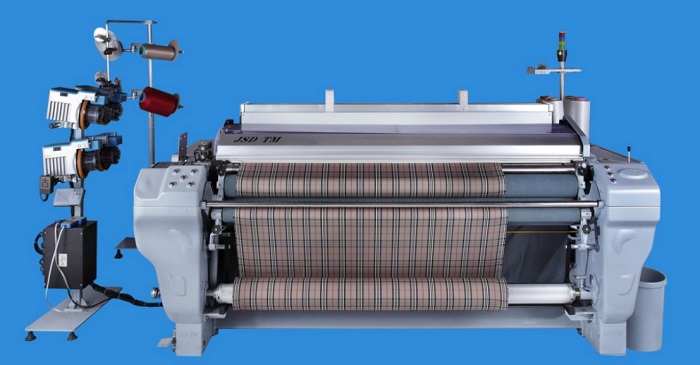
- Projectile loom: the weft is clamped by a small sheet shuttle with a clip, and the weft insertion is projected. The projectile loom has the advantages of stable weft insertion, excellent fabric quality, and less weft loops. It is suitable for the production of multi-color weft fabrics, fine and thick fabrics and wide fabrics.

In fact, after the fabric is weaved, there is another critical and time-consuming process-cloth inspection. At present, most of the fabric inspection links in factories are completed manually, which is a very big test for the professionalism, insight, patience, and care of the fabric inspectors. Because the manual inspection speed cannot be fast, the error rate is also high, the factory In order to produce qualified cloth, it is often necessary to hire a large number of cloth inspectors. A professionally qualified cloth inspector has a monthly salary of up to tens of thousands of yuan, and the labor cost is very high. Because manual inspection of cloth cannot be avoided, the production speed of cloth rolls has slowed down, and the production cost has also become higher.
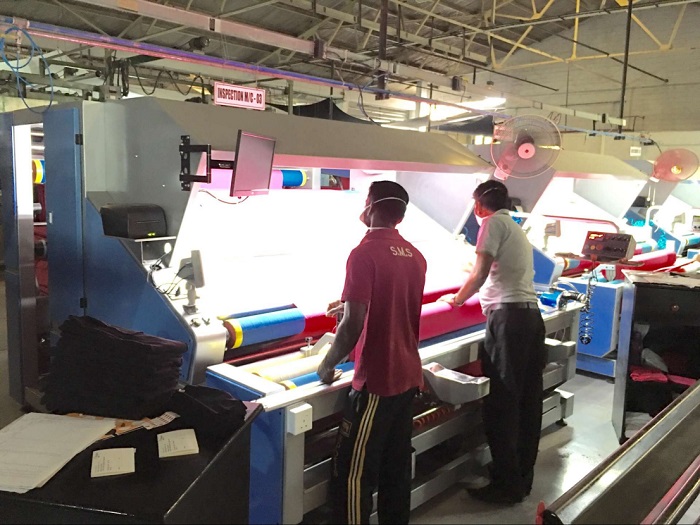

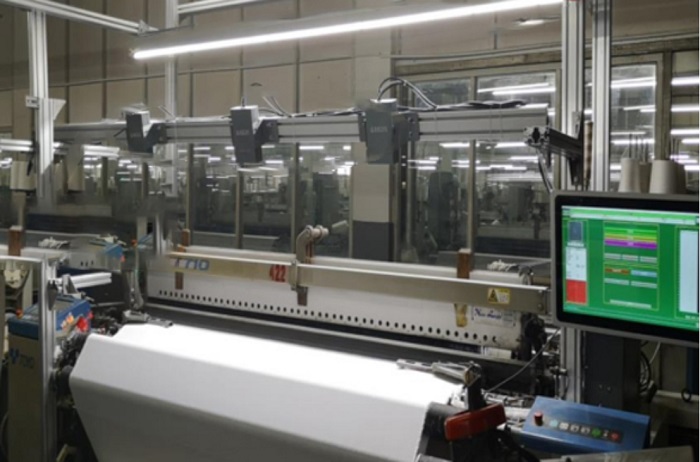
With 50 years of technical precipitation and design experience, the veteran machinery company Suntech has developed and designed rapier looms that not only intelligently integrate the five basic steps of weaving, but also the finished cloth can directly enter the automatic cloth inspection link, saving a lot of manpower and material resources. Time and cost.
Customers who have used Suntech rapier looms are full of praise for this loom, which can be called artificial intelligence in the loom industry. According to statistics, this loom can save 50% of labor costs and 50% on average, and increase production by 50%. Efficiency, in addition to automatic fabric inspection, it can also be controlled by PLC, automatic weft seeking, servo electronic warp let-off, servo electronic take-up, so that every step of the textile is intelligent, and the production speed is greatly improved. Welcome to inquire.





